The crankshaft sensor, also known as the crankshaft position sensor, plays a critical role in maintaining communication between your engine, crankshaft, and onboard computer. When this sensor fails, starting your car can be challenging and often unlikely. However, there are steps you can try to get the vehicle running long enough to drive it to a mechanic. This guide will cover the basics of the crankshaft sensor, how to attempt starting your car with a bad sensor, and when to seek professional help.
Key Points to Remember
- If possible, tow your vehicle to a mechanic instead of attempting to start it.
- Starting a car with a faulty crankshaft sensor is risky and often unsuccessful.
- To try starting the engine, disconnect the faulty sensor and spray starter fluid into the throttle body. Then, crank the engine.
- Signs of a bad crankshaft sensor include a check engine light, difficulty starting, and the car stalling or rattling when running.
- Replacing the sensor can be a complicated task. If you’re not confident, leave it to a professional mechanic.
What Does the Crankshaft Sensor Do?
- The crankshaft sensor ensures your engine operates efficiently and safely by monitoring the rotational speed and position of the crankshaft.
- It transmits this data to the engine control unit (ECU) and powertrain control module (PCM), helping the engine adjust to avoid issues like misfiring.
When the crankshaft sensor fails
- The ECU and PCM stop receiving critical data.
- Your vehicle may fail to start, as the engine cannot properly synchronize with the crankshaft.
- Even if the car starts, it’s prone to misfires or stalling.
Symptoms of a Bad Crankshaft Sensor
Check Engine Light: A faulty crankshaft sensor often triggers the check engine light because it sends incorrect or incomplete readings to the ECU.
Difficulty Starting
The car may refuse to start, as the sensor disrupts the engine’s communication with the computer.
Rattling or Stalling
If the engine does start, it may run rough, rattle, or stall unexpectedly.
Replacing the Crankshaft Sensor Yourself
If you’re comfortable with car repairs, follow these steps to replace the crankshaft sensor:
- Turn off the vehicle and disconnect the negative battery terminal.
- Locate the crankshaft sensor, typically found between the engine and transmission.
- Unplug the electrical connector from the sensor.
- Use a wrench to remove the bolts securing the sensor and carefully pull it out.
- Clean the surrounding area with a dry rag.
- Insert the new sensor, tighten the bolts, and reconnect the electrical connector.
- Reattach the battery terminal and start the vehicle.
Pro Tip
If the engine light remains on after the repair but the car runs smoothly, reset the error codes using an OBD-2 scanner.
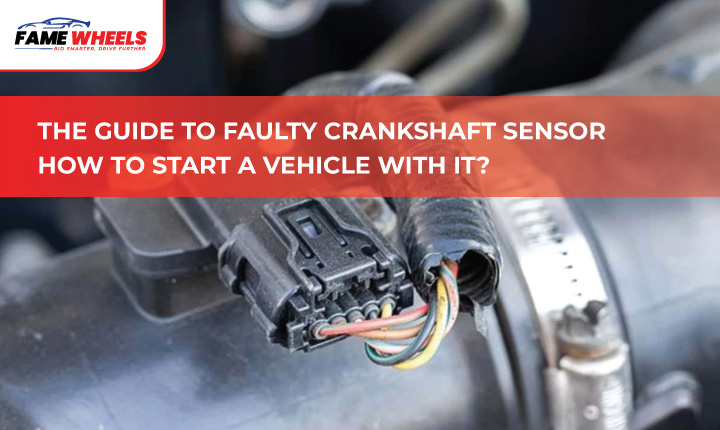
What Does a Crankshaft Sensor Look Like?
- Most crankshaft sensors are small L-shaped modules, measuring about 2–3 inches (5.1–7.6 cm) long, with one or two openings for bearings.
- Taking the proper steps to address a bad crankshaft sensor can save you from more significant engine issues down the road. If in doubt, consult a professional mechanic for diagnosis and repair.